 2018-02-01
2018-02-01  1105
1105
As an emerging energy source, biogas has become more and more widely used. It is strictly stipulated in China's environmental protection standards that when using biogas, the content of H2S in it must not exceed 20mg/m3. H2S must be removed as much as possible in industrial or domestic gas.

When biogas is produced from an anaerobic fermentation plant, especially when it is fermented at medium or high temperatures, it carries a large amount of H2S. As there is still a large amount of water vapor in the biogas, the water and the H2S in the biogas work together to accelerate the corrosion and plugging of metal pipes, valves and flowmeters. In addition, the SO2 generated after the combustion of H2S is combined with the water vapor in the combustion products to form sulfurous acid, which causes corrosion on the metal surface of the equipment and also causes pollution to the atmosphere and affects human health. Therefore, H2S must be removed before biogas is used.
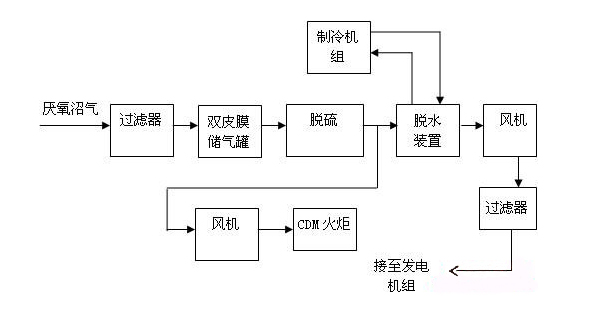
Dry desulfurization is a simple, high-efficiency, relatively low-cost desulfurization method and is generally suitable for desulfurization of biogas at a small amount and with a low concentration of hydrogen sulfide. The basic principle of a dry process for the removal of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from biogas is using O2 to oxidize H2S into sulfur or sulfur oxides, so it can also be referred to as dry oxidation. The dry process equipment consists of a filler put in a container with activated carbon, iron oxide, etc. After the gas goes at a low flow rate from one end through the inner packing layer of the container, H2S is oxidized into sulfur or sulfur oxides, while some remains in the filler layer and the purified gas is discharged from the other end of the container.
During the removal of H2S, the following chemical reactions occur with the desulfurizer:
Fe2O3 · H2O + 3 H2S = Fe2S3 + 4 H2O
 Current location:Home - Business Scope - Area of application
Current location:Home - Business Scope - Area of application
- Previous

-
Coal chemical industry
2018-02-01
- Next

-
Coking
2018-02-01

 Sales hot-line:0816-3736605
Sales hot-line:0816-3736605 E-mail:jysongwei@126.com
E-mail:jysongwei@126.com Address:No. 772, Laojun Road, Jiangyou, Sichuan
Address:No. 772, Laojun Road, Jiangyou, Sichuan

 QQ
QQ Tel
Tel Message
Message Share
Share Top
Top